
Green vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage and spinach, Chickpeas and kidney beans
Example of macro minerals skin#
Meat and poultry, Peanuts, Soya beans, BananasĬontribution to normal cysteine synthesis, Contribution to normal energy-yielding metabolism, Function of the nervous system, Contribution to normal homocysteine metabolism, Protein and glycogen metabolism, Contribution to normal psychological functions, Red blood cell formation, Function of the immune system, Reduction of tiredness and fatigue, Regulation of hormonal activityĮnergy-yielding metabolism, Function of the nervous system, Contribution to normal macronutrient metabolism, Contribution to normal psychological functions, Maintenance of normal hair, Maintenance of normal skin and mucous membranes Nutrient Reference Values (NRV) for adults 7Įnergy yielding metabolism, Function of the nervous system, Normal psychological function, Cardiac functionĬontribution to normal energy-yielding metabolism, Maintenance of the normal function of the nervous system, Maintenance of normal red blood cells, Maintenance of normal skin and mucous membrane,s Maintenance of normal vision, Contribution to normal metabolism of iron, Protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage, Reduction of tiredness and fatigueĬontribution to normal psychological functions, Contribution to normal energy-yielding metabolism, Function of the nervous system, Maintenance of normal skin and mucous membranes, Reduction of tiredness and fatigueĮnergy-yielding metabolism, Mental performance, Synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones, vitamin D and some neurotransmitters, Reduction of tiredness and fatigue These vitamins can be dissolved in water which means that any excess is flushed out of the body and they need to be replenished through the diet daily. Water-soluble vitamins – functions and sources The values are given here together with the foods that contain them. This is based on detailed reviews of the research and are applied to all products for adults 7. They are EU guidance levels on the daily amount of vitamin or mineral that the average healthy person needs. There are Nutrient Reference Values given for 13 vitamins and 14 minerals and these are used for food labelling. Micronutrients can be classified as water-soluble vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins, microminerals and trace minerals. What are the different types of micronutrients? The proven functions of some of the main micronutrients are detailed in the tables below 6. For example, magnesium is used for electrolyte balance, energy-yielding metabolism and many other functions 6. They are used in all the vital processes that the body carries out.
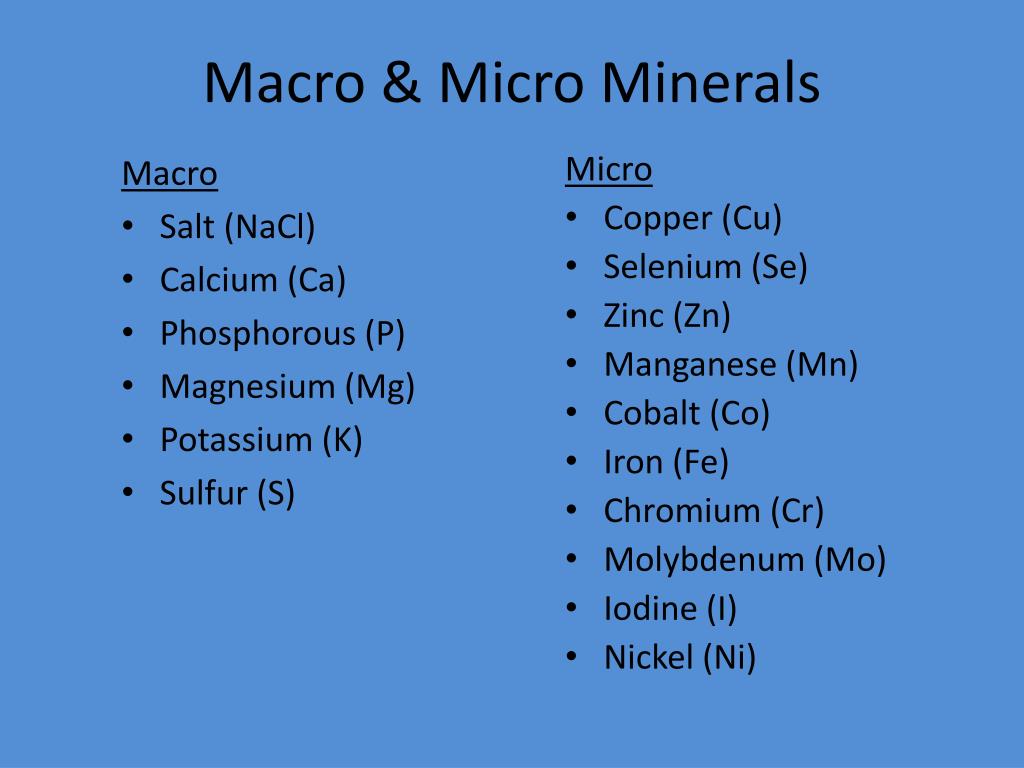
Example of macro minerals full#
Micronutrients are used for a huge range of different functions and the full extent of their role is still being discovered. What are the functions of micronutrients?
Vitamins and minerals are classified as micronutrients and common micronutrients examples include vitamin C and iron. It is also stressed that the benefit of micronutrients on the body is critical as they perform a range of functions, including enabling the body to produce enzymes, hormones and other substances needed for normal growth and development 5.īoth macro and micronutrients are essential but with micronutrients but as the name suggests, tiny quantities play a vital role in maintaining a healthy body. “vitamins and minerals needed by the body in very small amounts”

The World Health Organisation micronutrients definition is:

Apart from vitamin D, they cannot be made by the body and must be derived from our diet 4. Because they make up such a small fraction of what we eat, and because there are 27 different types, it can be hard to make sure that we get enough of them. In contrast, micronutrients (sometimes called vitamins and minerals) are required in very small amounts but benefit the body in very important ways. There are only three types of macronutrient they are proteins, carbohydrates and fats 3 although fibre is often also included. They make up the bulk of our food and it is not hard to get enough of them. Macronutrients are required by the human body in large quantities (macro means large) and are used for energy production as well as for growth and maintenance, transport and making more complex molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
